-
 RU
RU -
 EN
EN

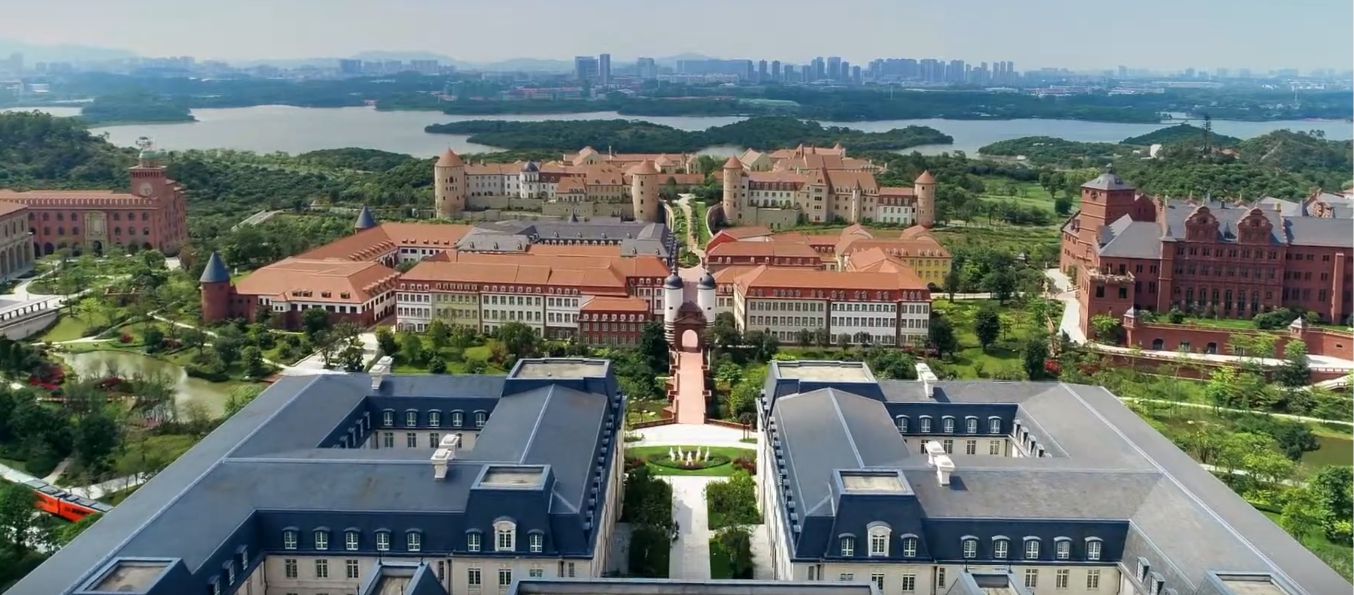
Join our Research & Development centers
Explore future together
Huawei's end-to-end portfolio of products, solutions and services are both competitive and secure. Through open collaboration with ecosystem partners, we create lasting value for our customers, working to empower people, enrich home life, and inspire innovation in organizations of all shapes and sizes.
At Huawei, innovation focuses on customer needs. We invest heavily in basic research, concentrating on technological breakthroughs that drive the world forward.
Mathematics, algorithms, software tools. Research on fundamental theory of maths, physics, chemistry, biology. (geometry, logic, thermodynamics, bionics, etc.)
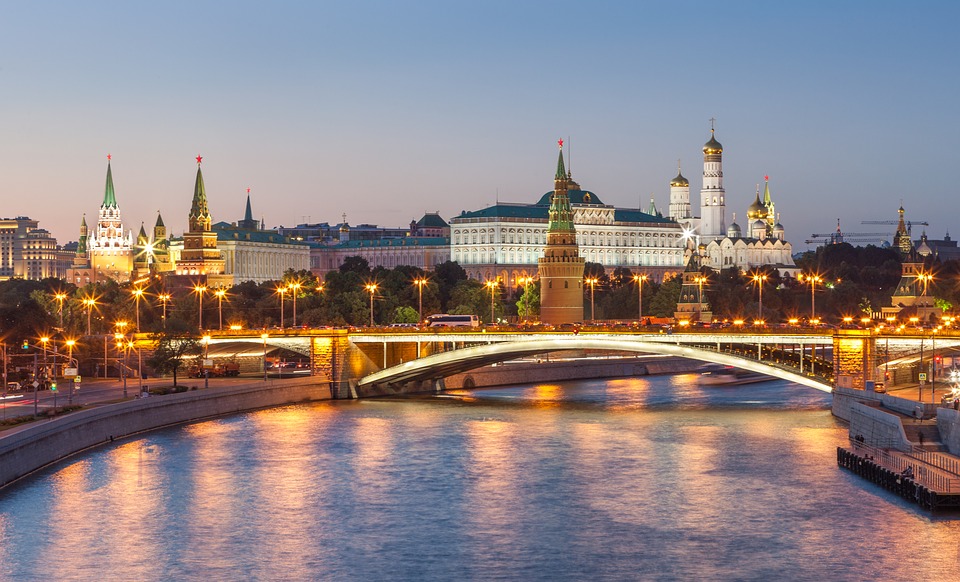 Moscow research center
Moscow research center  Saint-Petersburg research center
Saint-Petersburg research center  Nizhny Novgorod research center
Nizhny Novgorod research center  Novosibirsk research center
Novosibirsk research center  Minsk research center
Minsk research center Huawei is exploring out the smart future with leading partners, Huawei welcome more and more students to participate in future cutting-edge technical challenge.
<!-- If you would like to look for some specified positions click here -->
Huawei opens joint cultivation program in more than 8 universities since 2019. This program seeks to provide students a journey to explore the latest technologies from industry. In this process, it help students to understand the relationship between knowledge and industry technology application better, so that young students have more opportunities and experiences to think about what the future of digital transformation will be, what they could do and refine their skills.
<!--
If you would like to look for more study opportunity click here -->
The real world, outside of traditional bounds, is inherently nonlinear. The further evolution of Radio and Optical telecommunications requires sophisticated approaches for mitigation and compensation of nonlinear imperfections of devices and channels. In this lecture we will provide overview of typical nonlinear DSP algorithms, including crest factor reduction (CFR), digital predistortion (DPD) and nonlinear equalization (NLE). We will demonstrate on some examples how they increase performance and efficiency of telecommunication systems, reduce its cost and power consumption. Additionally we will show close connection of these topics with machine learning and neural networks, which is very popular now.
We live in the fast changing world - in the next decade we will become even more integrated with the numerous devices around us, on us and inside us. But all these devices will be managed by software and the most important part of the software is system software – the hidden part of the “iceberg” that actually enables everything else to work – operating systems, core algorithms, network stack, graphics engines, development tools. This talk will present Huawei’s vision on the next generation of such technologies that will “drive the world” in 2020s.
Massive-MIMO is one of the main trend in 5G networks, especially for mmWaves.
This lecture belongs to practical problems of massive-MIMO systems, which appear due to growth of spatial precision in wireless communication. But there are a lot of limitation to keep minimal error in parameter measurements to satisfy of the requirements for such precision systems. In the lecture we try to identify sources of the error, system robustness to these errors, and ways to minimize their impact. Also, it will be mentioned complexity problem for growth system dimensions. And how distributed approach can be used to overcome such problem.
The real world, outside of traditional bounds, is inherently nonlinear. The further evolution of Radio and Optical telecommunications requires sophisticated approaches for mitigation and compensation of nonlinear imperfections of devices and channels. In this lecture we will provide overview of typical nonlinear DSP algorithms, including crest factor reduction (CFR), digital predistortion (DPD) and nonlinear equalization (NLE). We will demonstrate on some examples how they increase performance and efficiency of telecommunication systems, reduce its cost and power consumption. Additionally we will show close connection of these topics with machine learning and neural networks, which is very popular now.
Speaker:
Pavel Plotnikov, Ph.D.
Principal engineer, Leader of Nonlinear Network team in Huawei R&D center, Moscow, Russia
We live in the fast changing world - in the next decade we will become even more integrated with the numerous devices around us, on us and inside us. But all these devices will be managed by software and the most important part of the software is system software – the hidden part of the “iceberg” that actually enables everything else to work – operating systems, core algorithms, network stack, graphics engines, development tools. This talk will present Huawei’s vision on the next generation of such technologies that will “drive the world” in 2020s.
Vladimir Rubanov is CTO for Software Engineering at Russian Huawei R&D and the leader of Operating Systems Lab. His former experience included executive and technical leadership positions at Rosplatforma, Virtuozzo (Parallels Group), ROSA (Russian Operating Systems and Applications) and ISPRAS (Institute for System Programming of the Russian Academy of Sciences).
Vladimir graduated (M.Sc.) from the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology with absolute honors (GPA 5.0 of 5). Has 50+ scientific publications, 100+ talks at the leading international conferences, academic rank of “Associate Professor in IT” and Ph.D. in Computer Science.
Massive-MIMO is one of the main trend in 5G networks, especially for mmWaves.
This lecture belongs to practical problems of massive-MIMO systems, which appear due to growth of spatial precision in wireless communication. But there are a lot of limitation to keep minimal error in parameter measurements to satisfy of the requirements for such precision systems. In the lecture we try to identify sources of the error, system robustness to these errors, and ways to minimize their impact. Also, it will be mentioned complexity problem for growth system dimensions. And how distributed approach can be used to overcome such problem.
Speaker: Lyashev Vladimir, Head of RTT Lab in MRC.
In this lecture we will overview modern question answering algorithms. The algorithms are classified by the source of the information for the answers. It could be knowledge bases (Knowledge Base Quesion Answering), large collection of question-answe pairs (ranking algorithms), the single document (reading comprehension), and even the whole Wikipwdia, or any other very large documents collection (Open Domain question answering). We will consider benefits and drawback of each approach and some examples of their work.
Irina Piontkovskaya, Head of NLP team in Huawei Noah's Ark, Huawei RRI.
The way we develop software today is incomparable with what we were doing twenty years ago: the languages are of a much higher level of abstraction; the availability of open source frameworks and libraries is exceptional; IDEs perfectly automate the majority of routine operations; compilers, linters, and builders are very powerful; continuous delivery practices are almost everywhere, and so on. However, this is not the final destination point yet. We are not even close! We, programmers, still make a lot of mistakes, our software products are full of bugs, and the success rate of software projects is going down every year (according to some industry reports). What is the next? What could be the “silver bullet” to save us from the complexity and instability of software development? We believe that Artificial Intelligence has a very good chance to become one. At the lecture we will discuss how exactly AI can be applied and where are the most interesting research problems to address.
Yegor Bugayenko is a seasoned software development expert, a designer of a few popular open-source Java frameworks, an author of “Elegant Objects” book series about object-oriented programming, a regular speaker at international software conferences, and a passionate advocate of high quality standards of software development.
The way we develop software today is incomparable with what we were doing twenty years ago: the languages are of a much higher level of abstraction; the availability of open source frameworks and libraries is exceptional; IDEs perfectly automate the majority of routine operations; compilers, linters, and builders are very powerful; continuous delivery practices are almost everywhere, and so on. However, this is not the final destination point yet. We are not even close! We, programmers, still make a lot of mistakes, our software products are full of bugs, and the success rate of software projects is going down every year (according to some industry reports). What is the next? What could be the “silver bullet” to save us from the complexity and instability of software development? We believe that Artificial Intelligence has a very good chance to become one. At the lecture we will discuss how exactly AI can be applied and where are the most interesting research problems to address.
Yegor Bugayenko is a seasoned software development expert, a designer of a few popular open-source Java frameworks, an author of “Elegant Objects” book series about object-oriented programming, a regular speaker at international software conferences, and a passionate advocate of high quality standards of software development.



